Have you ever been asked a question starting with: “Can you use R to…“, only to politely interrupt the inquisitor at this point to reply with something similar to “Yes, you can! R probably already has a package for this”.
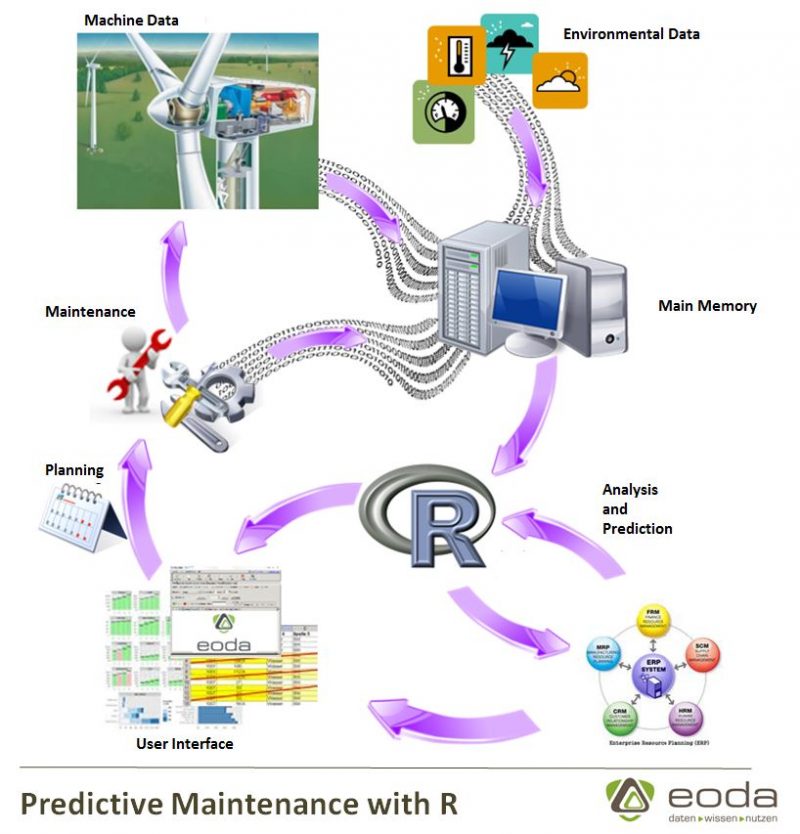
If this sounds familiar to you, you won’t be overly surprised to hear that R is now making advancements in the field of industrial production processes of the 21st century – respectively to the technological planning of production and maintenance processes.
The catchword in this context is Predictive Maintenance which represents the informatization of production processes away from only reactive repair mechanisms towards the realization of IT-based Smart Factories.
In industrial production, unforeseeable machine failures as well as performance drops or deterioration in quality because of defective system components can lead to severe shortness’ of supplies. In order to prevent this and to be able to survive in the global economy, organizations are increasingly focusing on the improvement, maintenance, and repair of their machinery.
What they need to successfully predict when a machine failure is likely to happen, or how to choose the best possible time to replace a wearing part of a critical production plant without causing a production stop or having to accept other cost disadvantages, is the implementation of a powerful analysis software. This is where R comes into play to put the innovative concept of Predictive Maintenance into practice to realize the hitherto unimaginable potential of a data analysis software for the optimization of industrial maintenance models and thereby changing the way organizations go about their process of machine maintenance.
As one of the best alternatives for e.g. the analysis and visualization of data and many benefits for Data Mining and Predictive Analytics, R can be tailored to the specific requirements of the condition monitoring and diagnostic technologies an organization might need.
While statistical methods such as Clustering, Classification, Regression Analysis or Event History Analysis lay the theoretical foundation for Predictive Maintenance strategies, by employing R, the entire process can be managed successfully: starting with the process of data collection, the analysis of the data to the preparation of a maintenance prognosis through to a clear visualization of the results.
Predictive modeling with R can be applied to a wide field of operations including Health Scoring, Lifespan Analysis as well as Time series models. The prediction of machinery failures in the semiconductor industry is only one specific example of how R uses the Random Forest CART (regression trees) to put the innovative concept of Predictive Maintenance into practice in order to significantly improve the process of machine maintenance with the result of the reduction of device downtime as well as of maintenance and manpower costs, and enhanced competitiveness in the specific industry sector.
Through the analysis of different machine data with R, the predictive power of the state of industrial plants is not only enhanced, but also provides the basis for an improved planning certainty as well as the efficient planning of repair and maintenance work.
Predictive Maintenance is the maintenance strategy of the future, and the programming language R with its endless possibilities is a key tool for its successful realization in times of Smart Factories and the Internet of Things.
If this made you curious and you want to know more about the potential and possibilities of R for business models in times of the digital industry, you might be interested to learn that eoda recently published a Whitepaper (in German) on the topic: “Predictive Maintenance (mit R) – Leistung immer und überall dank vorausschauender Wartung basierend auf statistischen Modellen”. In the Whitepaper the data analysis experts discuss the context and chances of R for Predictive Maintenance on the basis of statistical models and examples of possible fields of application.
This way.